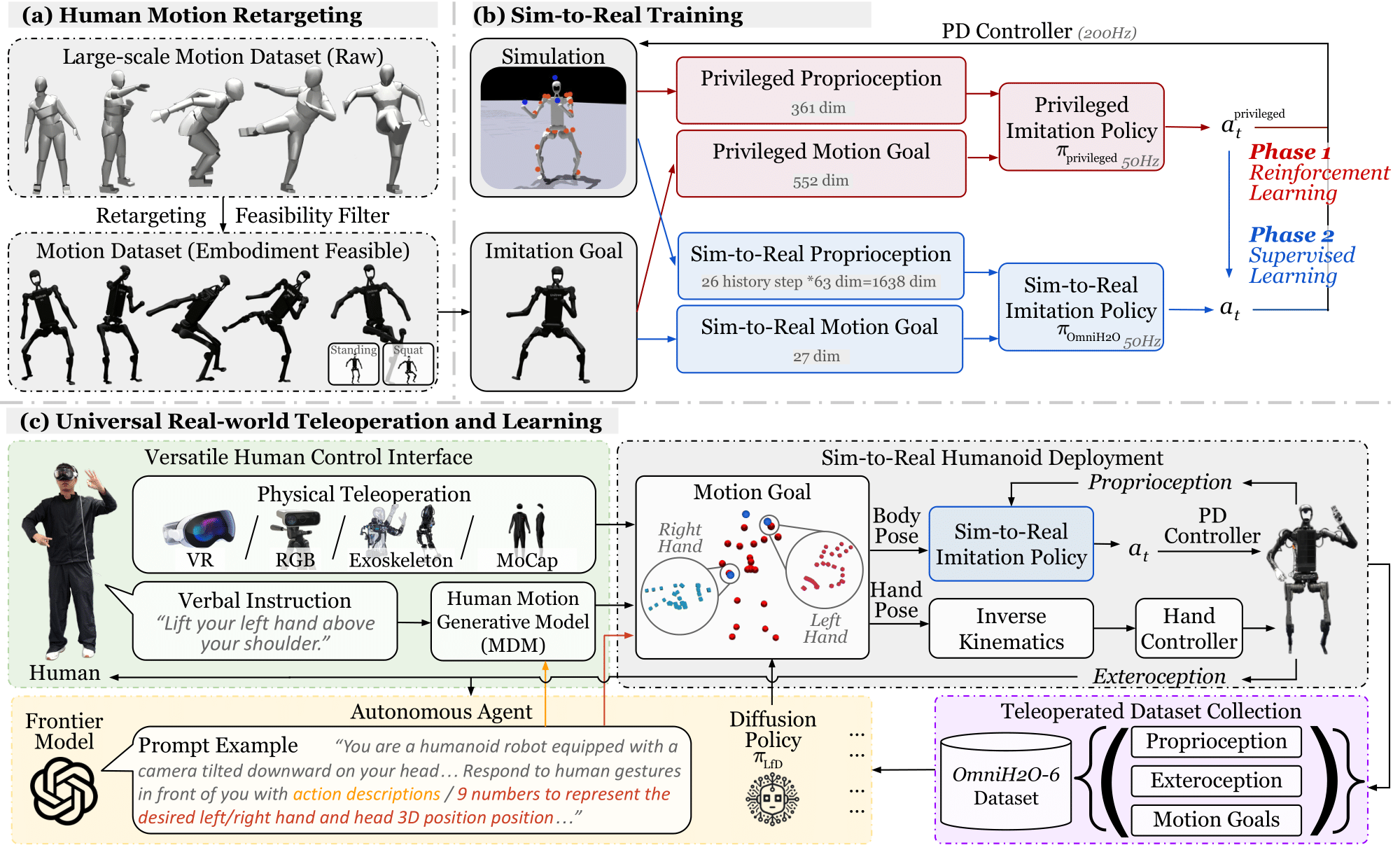
We present OmniH2O (Omni Human-to-Humanoid), a learning-based system for whole-body humanoid teleoperation and autonomy. Using kinematic pose as a universal control interface, OmniH2O enables various ways for a human to control a full-sized humanoid with dexterous hands, including using real-time teleoperation through VR headset, verbal instruction, and RGB camera. OmniH2O also enables full autonomy by learning from teleoperated demonstrations or integrating with frontier models such as GPT-4. OmniH2O demonstrates versatility and dexterity in various real-world whole-body tasks through teleoperation or autonomy, such as playing multiple sports, moving and manipulating objects, and interacting with humans. We develop an RL-based sim-to-real pipeline, which involves large-scale retargeting and augmentation of human motion datasets, learning a real-world deployable policy with sparse sensor input by imitating a privileged teacher policy, and reward designs to enhance robustness and stability. We release the first humanoid whole-body control dataset, OmniH2O-6, containing six everyday tasks, and demonstrate humanoid whole-body skill learning from teleoperated datasets.